Past progressive
Forms
was/were + -ing
- I was working.
- Were you listening to me?
- She was not trying.
For details of question structures, (see here). For negatives, (see here).
For passive forms (e.g. Work was being done), (see here).
For double letters in words like sitting, stopping, (see here).
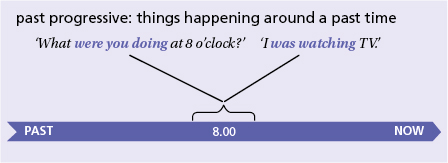
Use: What were you doing at eight o’clock?
We use the past progressive to say that something was in progress (going on) around a particular past time.
- ‘What were you doing at eight o’clock yesterday evening?’ ‘I was watching TV. ’ (not
What did you do …? I watched TV.) - When I got up this morning the sun was shining, the birds were singing, … (not
… the sun shone, the birds sang …)
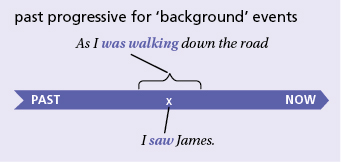
Past progressive and simple past: ‘background’ events
We often use the past progressive together with a simple past tense. The past progressive refers to a longer ‘background’ action or situation; the simple past refers to a shorter action or event that happened in the middle of the longer action, or that interrupted it.
- As I was walking down the road, I saw James.
- The phone rang while I was having dinner.
- Mozart died while he was composing the Requiem.
Not used for repeated actions
The past progressive is not the normal tense for talking about repeated or habitual past actions. The simple past is usually used with this meaning.
- I rang the bell six times. (not
I was ringing the bell six times.) - When I was a child we walked to school. (not
… we were walking to school.)
However, the past progressive is possible if the repeated actions form a ‘background’ for the main action.
- At the time when it happened, I was travelling to New York a lot.
Non-progressive verbs: She said she believed
Some verbs are not often used in progressive forms (see here).
- She said she believed Joe was dying. (not
She said she was believing …)
Used for shorter, temporary actions and situations
The past progressive, like other progressive forms (see here), is used for temporary actions and situations. When we talk about longer, more permanent situations we use the simple past. Compare:
- It happened while I was living in Eastbourne last year.
I lived in London for ten years while I was a child. - When I got home, water was running down the kitchen walls.
When they first discovered the river, they thought it ran into the Atlantic.
Special uses
Because we often use the past progressive to talk about something that is a ‘background’, not the main ‘news’, we can make something seem less important by using this tense. Compare:
- I had lunch with the President yesterday. (important piece of news)
- I was having lunch with the President yesterday, and she said … (as if there was nothing special for the speaker about lunching with the President)
The past progressive is quite often used with verbs of saying: this gives more relative importance to the following verb – to what is said.
- Jack was saying that he still can’t find a job.
With always, continually and similar words, the past progressive can be used for things that happened repeatedly and unexpectedly or in an unplanned way (see here).
- Aunt Lucy was always turning up without warning and bringing us presents.
- I didn’t like him – he was continually borrowing money.
For the ‘distancing’ use of past progressives (e.g. I was wondering whether you’d like to come out with me this evening), (see here).